One In Four Workers Say They Are Working Entirely From Home: Gallup Tyler Durden Tue, 09/01/2020 - 23:25
By Jeffrey Jones of Gallup,
The coronavirus pandemic has led to a surge in remote work. However, that surge is more apparent in the number of remote working days for telecommuters than in the number of workers moving from on-site to at-home work.
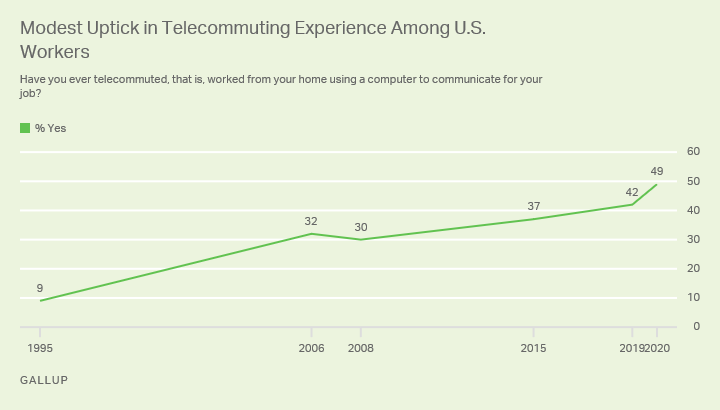
Since Gallup last asked about remote work in October 2019, there has been a modest uptick in the percentage of U.S. workers who report having ever telecommuted for work, from 42% to 49%. The recent figures demonstrate the growth in remote work over recent decades from 9% in Gallup's initial measurement in 1995.
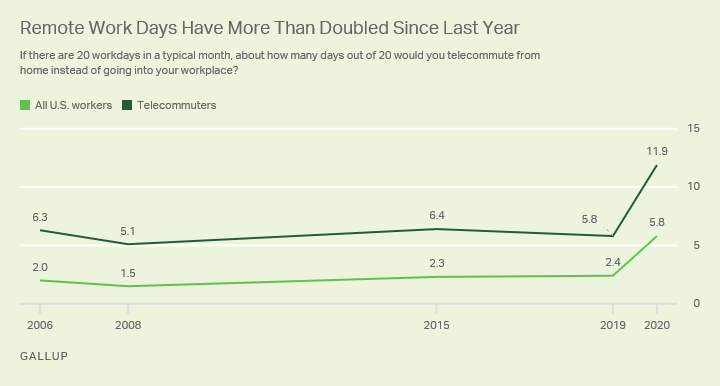
While the percentage of U.S. workers who have telecommuted has changed modestly, the average number of workdays telecommuters are working from home has more than doubled, from 5.8 days per month last fall to 11.9 days currently. Among all U.S. workers, the average number of telecommuting days has also more than doubled, from 2.4 per month to 5.8.
These results are based on Gallup's annual Work and Education poll, conducted July 30-Aug. 12.
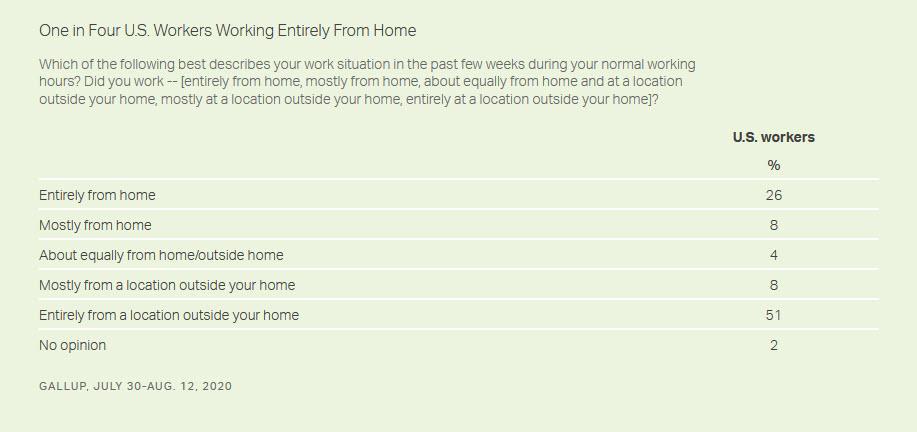
The poll finds 26% of U.S. workers currently saying they have worked entirely from home in recent weeks, while 51% are working entirely from a location outside their home, with one in five reporting a mix of on-site and remote work.
Nearly half of those who have ever telecommuted, 45%, say they have been working entirely from home in recent weeks, with another 14% working mostly from home. This question had not been asked previously, so it is not possible to know how those figures compare with before the pandemic.
However, 13% of telecommuters and 5% of all workers in 2019 said they worked from home 20 days a month (assuming 20 monthly workdays). Now, the figures are 45% and 22%, respectively.
College Graduates Much More Likely to Work Remotely
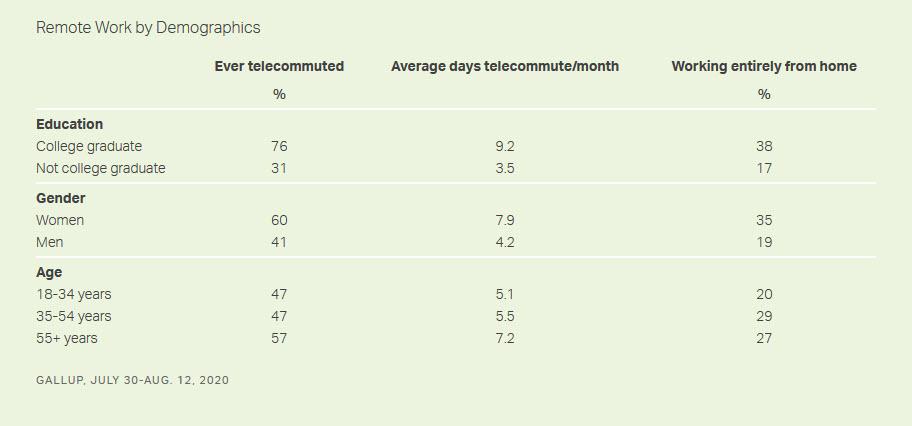
As might be expected, telecommuting is much more common among Americans with a college degree than those without one. Employed college graduates are more than twice as likely as employees without a college degree to work remotely. This is seen in the percentages reporting that they have ever telecommuted, as well as in the number of days they report working remotely and in their self-reports of whether they are currently working entirely from home.
The survey also shows that working women are more likely than working men to be performing their job functions remotely.
The differences between younger and older workers' likelihood to work remotely are not statistically meaningful.
An analysis of prior Gallup data on occupation finds that the vast majority of college graduates work in what can be considered white-collar occupations, and that women are much more likely than men to do so.
Last year, an average of 63% of college graduates versus 29% of college nongraduates had ever telecommuted, so the growth in telecommuting has come almost entirely among those with higher educational attainment. Also, before this year, men and women were about equally likely to say they had ever telecommuted for work. The emerging gender gap in remote work probably reflects women's greater presence in white-collar than blue-collar jobs.
Implications
The widespread closure of businesses and schools to control the spread of the coronavirus sent unemployment soaring. The jobs situation would have been much worse if not for advances in technology that allow many workers to complete their work remotely. Close to half of U.S. workers have now taken advantage of opportunities to telecommute, and currently about one-quarter are doing so every workday.
Of course, not every job can be done remotely; therefore, the growth of telecommuting has a ceiling. Half of U.S. workers currently say they do their job entirely at a location outside their home. Given this, and that half of U.S. workers report they have never telecommuted, the growth in the proportion of the workforce that could telecommute may have reached that ceiling during the pandemic. Further growth in remote work may thus come in the amount of time workers spend outside the office or work site, rather than in the number of workers who do so.
Having an expanded remote workforce alters the dynamics for employers in many ways. Remote work changes the considerations on where employers can find and attract new hires. For example, flexible work arrangements have special appeal to millennials and women. But remote work also can create both challenges and opportunities when it comes to worker engagement, worker productivity and maintaining company culture. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the trend toward remote work and has made companies' policies toward it even more crucial to their success.
https://ift.tt/2EOOV39
from ZeroHedge News https://ift.tt/2EOOV39
via IFTTT





0 comments
Post a Comment