August Payrolls Preview: It Will Be A Miss, The Question Is How Big
Summary: The consensus looks for the pace of hiring to cool in August, especially after Wednesday's disastrous ADP report, although the short-term trend rates are still likely to improve; if the consensus is correct, it may offer further accumulated evidence that the labor market is making progress towards the Fed's 'substantial' threshold where it will feel comfortable in scaling back its asset purchases, according to Newsquawk..
Key expectations:
- Headline non-farm payrolls are expected to print 725k (prev. 943k).
- The unemployment rate is expected to decline by 0.2% to 5.2%, although this figure may not give a true reflection of the labor market;
- Analysts will be focused on the participation rate (which rose to 61.7% in July from 61.6% in June vs 63.2% pre-pandemic), the U6 measure of underemployment (which fell to 9.2% in July from 9.8% in June vs 7.0% pre-pandemic), and the employment-population ratio (which rose to 58.4% in July from 58.0% in June vs 61.1% pre-pandemic).
- Average hourly earnings are expected to rise 0.3% M/M, down from 0.4% in July, and 4.0% Y/Y.
Labor market gauges have been mixed in August: while ADP's private payrolls disappointed expectations (again), the weekly initial jobless claims and continuing claims fell to a new post-pandemic low. Other metrics, however, offer a gloomier assessment: the ISM and Markit manufacturing surveys allude to a cooling in labor market conditions, with the Delta variant being cited as a reason for the softer pace of hiring. Given that the jobs data will be framed within the context of the Fed's policy reaction, many analysts have been suggesting a 'good data is bad for the prospects of further accommodation' playbook, and vice versa; however, this strategy was not seen in wake of the disappointing ADP data this week. Many argue that the market has already moved on from the timing of the taper announcement – assumed to be in Q4 before implementation late this year or early next – and focus is on the pace of the reductions and the duration of the taper, and the August jobs data is not likely to inform the latter two meaningfully.
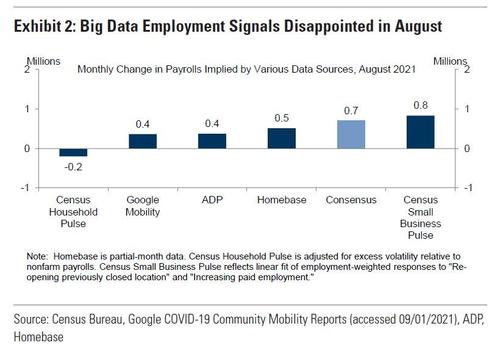
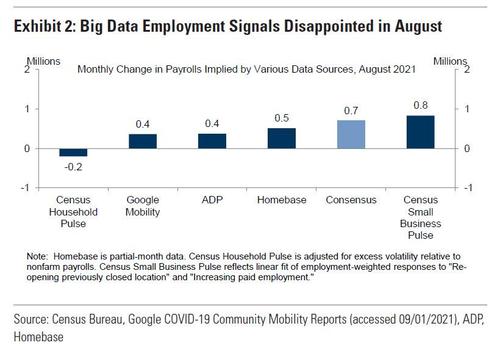
While Consensus remains surprisingly bullish, Goldman's forecast was recently slashed to just 500K, about a third lower than consensus of 725K. As the bank explains, "while the seasonal hurdle is relatively low in August, the monthly pace and cross-section of Big Data employment indicators are consistent with a sizeable drag from the Delta variant." Specifically, the bank notes that high-frequency data on the labor market were disappointing between the July and August survey weeks with all of the indicators we track consistent with a slowdown from the 943k July pace. Only one of the five measures Goldman tracks indicated an underlying job gain in excess of consensus (Census Small Business Pulse, +0.8mn). On the positive side, Goldman expects the reopening of schools to boost job growth by around 150k in tomorrow’s report.
POLICY FOCUS: Many Fed officials want to see further accumulated evidence that the labor market is progressing towards its 'substantial further progress' threshold for tapering asset purchases before they commit to a timeline for scaling back these purchases, as well as the modalities of how the taper will look. The August jobs data will be eyed within this context, with analysts suggesting that a weak reading will allow the Fed more time to shape its views, while a stronger-than-expected report will add urgency to a process that some Fed officials want wrapped-up by mid-2022. The Fed has been framing the post-pandemic upside in inflation as transitory, although not everyone is convinced.
SLACK: Headline non-farm payrolls are expected to print 728k (prev. 943k) in August; private payrolls are seen at 665k (prev. 703k), and government payrolls are seen at 25k (prev. 27k). The unemployment rate is expected to decline to 5.2% from 5.4%; many officials do not think that the headline unemployment rate is truly indicative of the health of the labour market, and in recent months, have been monitoring measures like the participation rate (which rose to 61.7% in July from 61.6% in June vs 63.2% pre-pandemic), the U6 measure of underemployment (which fell to 9.2% in July from 9.8% in June vs 7.0% pre-pandemic), and the employment-population ratio (which rose to 58.4% in July from 58.0% in June vs 61.1% pre-pandemic) which all offer better insight into the progress being made in eroding the slack seen since the pandemic.
TREND RATES: There are still 5.7mln fewer Americans in employment compared to pre-pandemic levels in February 2020. The Fed does not specifically quantify what 'substantial further progress' means; market participants have argued that, at minimum, it should mean a continuation of current trends, if not an improving trend rate. The short-term trends improved in the July data; the 3-month trend rate stood at 832k in July (vs 607k trend in the 3-months through June); the 6-month trend rate stood at 681k in July (vs the 563k in the 3-months through June); but the 12-month trend rate was 605k in July (vs 670k in the 12-months through June). If the August consensus expectation of 728k was realised, the 3- month and 6-month trend rates would improve again, possibly giving Fed officials evidence of accumulated progress towards the 'substantial further progress' threshold.
WAGES: Average hourly earnings are seen rising +0.3% M/M (prev. +0.4% M/M), though the annualized measure is seen unchanged at 4.0% Y/Y; the average workweek is expected to be unchanged at 34.8hrs. Analysts will be carefully monitoring the average hourly earnings measures; the argument is that higher prices may stoke consumer inflation expectations, as seen in recent consumer confidence reports, and will result in higher compensation as workers demand more cash amid rising prices; analysts say that this would add to evidence that inflation is more persistent than the Fed is currently admitting to.
ADP: The private payrolls survey by ADP disappointed expectations, showing just 374k jobs were added to the US economy in August; analysts were expecting 613k, following the (also) disappointing 326k it reported in July. ADP attributed the weak August report to the Delta variant; Moody's Analytics said "the Delta variant appears to have dented the job market recovery," but "job growth remains strong, but well-off the pace of recent months, and job growth remains inextricably tied to the path of the pandemic." Fed officials have recently been more sanguine on the impact of Delta, although some officials have argued that the Fed is still capable of tweaking policy if the pandemic once again became more persistent. NOTE: The ADP data uses previous official BLS data within its methodology; that July BLS data was strong relative to expectations, so does allude to a more tepid pace of hiring in August, although desks continue to note the tenuous relationship that the ADP data has in signalling the official BLS data; last month, for instance, the ADP flagged a weaker jobs report, although the official data surprised to the upside.
INITIAL JOBLESS CLAIMS: Weekly claims data that coincides with the traditional BLS survey window showed claims falling to a post-pandemic low at 349k; the four-week moving average also declined relative to the July survey window, both boding well for the official jobs report. The continuing claims data which coincides with the traditional BLS survey window also fell to a post-pandemic low at 2.862mln (vs 3.296mln heading into the July jobs data). Pantheon Macroeconomics said that the claims numbers are now finally free of the distortions caused by the automakers' retooling shutdowns and the trend is still falling, which suggests that the surge in COVID cases had not yet triggered an increase in layoffs. "These data, however, tell us nothing about the pace of gross hiring, and it’s entirely possible that firms’ first reaction to the Delta wave has been to slow the pace of recruitment, before taking the more difficult decision to let go existing staff," Pantheon said, "still, these data are encouraging." Other desks also point out that the claims data only gives insight into workers being laid off (and is essentially corroborated by Challenger's lay-offs data, which fell to the lowest since June 1997), whereas some argue that the labour market weakness seen of late is likely a function of slowing hiring amid the spread of the Delta variant, which is more reflected in surveys.
BUSINESS SURVEYS: The business survey data only offers a partial glimpse of the labour market this month, given that the Services ISM and Markit's Final Services PMI for August are both set for release after the jobs report (NOTE: the flash services data from Markit showed employment falling by 2.5 points to 50.8). The ISM manufacturing report saw its employment sub-index tumble by almost 4 points into contractionary territory at 49.0, with the survey noting that new surges of COVID-19 were adding to pandemic-related issues, like worker absenteeism, short-term shutdowns due to parts shortages, as well as difficulties in filling open positions and overseas supply chain problems. That said, the report also said that companies were still struggling to meet labour-management plans, but despite a contracting index, there were positive signs compared to recent months, partly mitigating the gloom implied by the index itself. Meanwhile, Markit's manufacturing PMI alluded to employment growth easing as firms struggled to retain staff and find suitable candidates for current vacancies.
ARGUING FOR A WEAKER-THAN-EXPECTED REPORT:
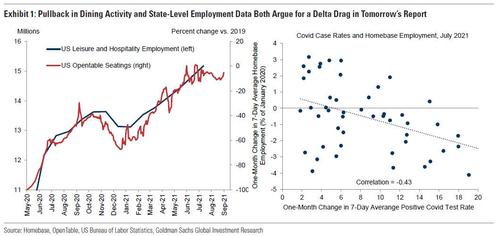
- Delta variant. Unlike in the first month of the covid resurgence, the Delta variant now appears to be affecting services consumption and the labor market. The revival of the CDC’s mask recommendation on July 27 occurred after the July payroll survey week had ended, which would be consistent with a drag in tomorrow’s report despite the strong gains in the previous one. As shown in the left panel of Exhibit 1, restaurant seatings on Open Table pulled back at the turn of the month, falling to 89% of their 2019 levels during the August survey week, compared to 95% in the July survey week. This would argue for a pause or pullback in US leisure and hospitality employment in tomorrow’s report. Additionally, as shown in the right panel, rising infection rates were associated with weaker employment growth in the state cross-section of the Homebase dataset, consistent with a negative Delta impact on labor demand, labor supply, or both.
- Big Data. High-frequency data on the labor market were disappointing between the July and August survey weeks (see Exhibit 2), with all of the indicators we track consistent with a slowdown from the 943k July pace. Only one of the five measures we track indicates an underlying job gain in excess of consensus (Census Small Business Pulse, +0.8mn), though we acknowledge that the track record for Big Data indicators during the crisis has been mixed.
- ADP. Private sector employment in the ADP report increased by 374k in August, below consensus expectations for a 625k gain. Because the statistical inputs to the ADP model probably boosted their jobs estimate, we believe the underlying ADP sample showed only modest gains in the month.
ARGUING FOR A STRONGER-THAN-EXPECTED REPORT
- School reopening. We expect a roughly 150k boost from the reopening of schools, as many teachers and support staff return for the fall school year (some of whom were not working at the end of the prior one). While a pace of reopening similar to August 2020would contribute nearly 300k jobs (mom sa), the level of education employment is 600khigher a year later, and we believe some janitors and support staff did not return due to capacity restrictions and hybrid teaching models.
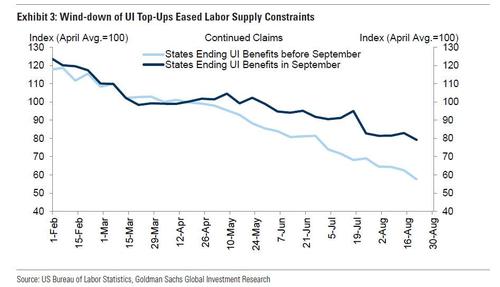
- Wind-down of Top-ups. The expiration of federal benefits in some states has boosted labor supply and job-finding rates. Federal benefits were partially or fully curtailed in half of US states (representing 29% of the outstanding job losses since the start of the pandemic) in June and early July. And encouragingly, continuing claims have continued to decline more quickly in these states (by roughly 150k relative to the trend in all other states in the August payroll month).
- Seasonality. The August seasonal hurdle is relatively low: the BLS adjustment factors generally assume a 100-200k decline in private payrolls (which exclude public schools),compared to +0.5mn over the previous four months.
- Job availability. The Conference Board labor differential—the difference between the percent of respondents saying jobs are plentiful and those saying jobs are hard to get—decreased by 1.3pt to +42.8 in August but remains at a high level. Additionally, job openings increased by 590k to a record high in June, according to the JOLTS report.
- Jobless claims. Initial jobless claims edged down during the August payroll month,averaging 355k per week vs. 393k in July. Continuing claims also decreased, averaging2,840k in August vs. 3,140k in July. Across all employee programs including emergency benefits, continuing claims remained roughly unchanged between the payroll survey weeks.
NEUTRAL/MIXED FACTORS:
- Employer surveys. The employment component of the ISM Manufacturing Index fell into contractionary territory (-3.9pt to 49.0). The employment component of our manufacturing survey tracker also decreased (-0.8pt to 58.3), but the employment component of our services survey tracker increased (+0.1pt to 54.9). The employment component of the GSAI increased by 2.8pt to 70.0.
- Job cuts. Announced layoffs reported by Challenger, Gray & Christmas decreased by1% in August after decreasing by 13% in July (mom, SA by GS). Layoffs were at the lowest level since 1993.
REACTION: Citi argues that given still net-long broader USD positions, any miss relative to the consensus may buoy Treasuries (as traders reason that the Fed would remain accommodative for longer), and any decline in yields would likely accelerate the Dollar's recent underperformance. "A 'goldilocks' release that entails a slight miss would be most ideal for risk assets heading into an extended weekend," but the bigger picture Citi says is that "the broader taper narrative will not have long-lasting market implications given broad expectations for a Q4 conclusion; nonetheless, the interim run-up will see taper talk as a persistent albeit fading influence on market moves."
https://ift.tt/38E8LcJ
from ZeroHedge News https://ift.tt/38E8LcJ
via IFTTT

0 comments
Post a Comment